Smartphone Market Maturation, New Strategy Urgently Needed for Survival
The anticipated global decline in smartphone shipments for 2023, expected to be the lowest in a decade, signals a significant shift towards a saturation point. This development underscores the need for both device manufacturers and electronic component producers to adopt 'new strategies' to navigate this changing landscape.
12 October 2023 - It is clear that the smartphone market is maturing. Global shipments in 2023 are expected to be the lowest in the past 10 years. A number of Japanese device manufacturers are scaling back or abandoning their business. Additionally, with device shipments sluggish, there is a possibility that pressure on electronic component manufacturers to lower prices will increase future intensity. In order to survive the smartphone market that has entered a new normal, both device manufacturers and electronic component manufacturers will need new strategies.
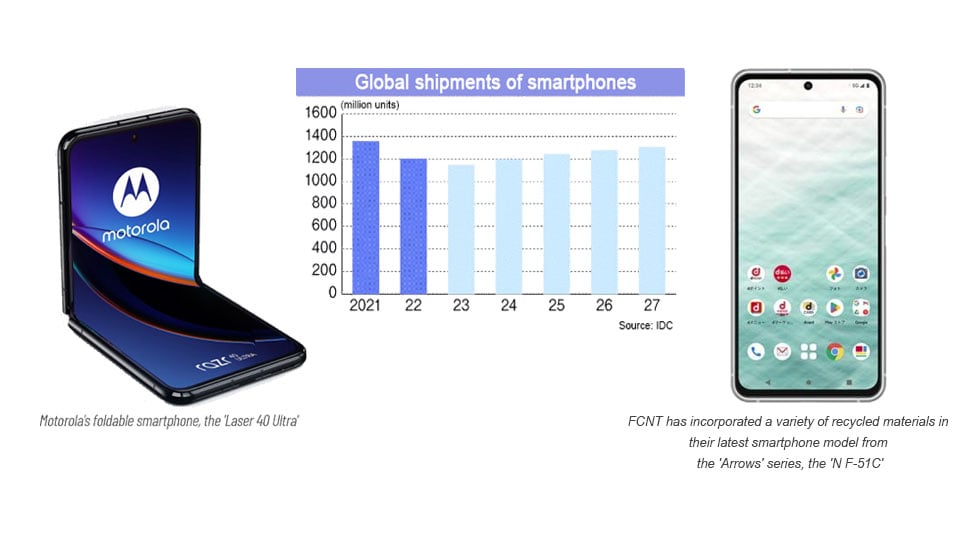
Mobile device: Global shipments hit “lowest level” in 2023
In 2023, Japanese mobile device manufacturers decided to withdraw or downsize their businesses one after another. Kyocera plans to partially withdraw from consumer smartphones by the end of March 2025 and focus on products such as high-durability smartphones that have high corporate demand. Balmuda also decided to withdraw from the smartphone business due to difficulties in developing the next model.
Three other companies, including FCNT (formerly Fujitsu Connected Technologies), which took over Fujitsu’s mobile terminal business, applied to the Tokyo District Court at the end of May for application of the Civil Rehabilitation Law.
Yano Research Institute in Tokyo points out that “It is difficult for manufacturers without differentiating factors to survive.” In fact, Sony has been able to continue its business by developing image sensors and differentiating itself from other companies through camera performance. However, domestic manufacturers, including Kyocera and Sharp, have not been able to increase their presence in the global market.
Regarding FCNT, China’s Lenovo Group decided to take over the business and resumed device development, sales, and services on October 1st. FCNT says, “We are at the stage where we have begun incorporating synergies with Lenovo into strategies and measures.” For Lenovo, “It’s an advantage to be able to acquire FCNT’s connection with NTT Docomo,” said Hideaki Yokota, director and deputy director of MM Research Institute.
Reasons behind the current predicament of Japanese mobile device manufacturers include rising raw material prices and the continued depreciation of the yen. What cannot be overlooked is the current stagnation in smartphone demand. US research firm IDC estimates that global smartphone shipments in 2023 will be 1.15 billion units, down 4.7% from the previous year. This is expected to be the lowest level in the past 10 years.
Electronic components aim to create differentiation
Manufacturers in Japan and overseas are trying to create demand by promoting ease of use and environmental friendliness. Apple has switched to a general-purpose “USB Type C” terminal.” Motorola Mobility, a subsidiary of Lenovo, has also launched a foldable smartphone in the Japanese market. Sharp and FCNT are promoting smartphones that use a higher percentage of recycled plastic. FCNT says, “This is the first time that we have publicly announced the percentage of recycled materials used.”

FCNT has incorporated a variety of recycled materials in their latest smartphone model from the 'Arrows' series, the 'N F-51C'
In order to stimulate demand, it is essential not only to improve terminals but also to support the development of communication technology. The key is the further spread of fifth-generation communications (5G). Multiple connections can be made simultaneously, enabling high-speed, large-capacity, and low-latency communications. MM Research Institute’s Deputy Director Yokota predicts, “With the availability of 5G networks, new content and devices will emerge.” which will lead to an increase in consumers’ desire to purchase smartphones.
Replacement cycles are extended and pressure to lower prices intensifies
“Price reduction is once again at the top of Apple’s wish list.” An official at an electronic parts manufacturer that does business with the company describes the current situation as follows. Apple released the iPhone 15 in September, and the dollar price of its top model has increased for the first time in five years. However, this person points out that the pressure on parts manufacturers to lower prices has increased compared to the past two years during the coronavirus pandemic.
Before the coronavirus pandemic, Apple was known for its strict price demands, backed by its extraordinary procurement power. While there is an advantage in using cutting-edge parts, many parts manufacturers have had the experience of being asked to cut prices by double digits or being forced to compete with multiple competitors for general-purpose products. “The supply chain has been disrupted due to the coronavirus pandemic, and securing parts has become a top priority. There may be some parts whose prices have barely dropped for about two years.” Said an official.
Now that there is a growing awareness that the end of the coronavirus pandemic is nearing and the supply chain is normalizing, price demands have also begun to return to pre-coronavirus levels. An official said. “The price reduction for parts other than general-purpose items was limited to 1 digit per cent, and it appears that there was no ‘backlog’ due to the coronavirus pandemic.” added. “We don’t know Apple’s parts procurement policy from next year onwards.” He says. This is because the growth of the smartphone market as a whole has stalled.
Hong Kong-based research firm Counterpoint Research predicted that global smartphone shipments in 2023 will be the lowest in the past 10 years. Inflation has caused consumers to be cautious about their spending, but the more serious structural aspect is that the replacement cycle for smartphones is lengthening due to the maturation of smartphone functions and the expansion of the second-hand market.
Amid sluggish market growth, Apple has pursued a strategy of increasing unit prices rather than unit sales. However, there is no point in raising unit prices if there is no profit. There are reports that local governments and state-owned enterprises in China, one of China’s largest markets, are starting to restrict the use of foreign smartphones, including iPhones, and there are developments that are putting more pressure on component manufacturers to lower prices than ever before. Even if the smartphone market does not shrink rapidly in the short term, it may become difficult for electronic component manufacturers to maintain the same profit margins for smartphone products as before.
The key to increasing market share and expanding sales to peripheral devices
One of the measures that electronic component manufacturers can take is to increase their market share. TDK has introduced battery products with increased energy density by introducing silicon negative electrodes.
Some iPhone 15 models are now capable of shooting 3D video, and it has been suggested that they will be compatible with Apple’s goggle-type device “Vision Pro.” There appears to be a strategy to improve the overall price/performance ratio by connecting it with peripheral devices, leading to increased sales of each. Although it is unclear whether the Vision Pro, which has a higher unit price than the iPhone, can be expected to sell as expected, it could lead to market expansion for electronic component manufacturers.
It is also effective in responding to new demands created by changes in the way smartphones are used. Google is expanding services such as image processing using generative artificial intelligence (AI) on its new smartphones. Equipped with a uniquely developed semiconductor, it can combine multiple images to create a single optimal image. Although some people say, “We cannot expect demand for cutting-edge electronic components unless they are equipped with semiconductors that are higher performance than the iPhone.” Electronic component manufacturers will first sell smartphones other than the iPhone with new products. “I think we need an approach that aims to introduce new technology and adopt it for the iPhone once it reaches maturity,” says Manabu Akizuki, an analyst at Nomura Securities.






